000
As a great discovery in the 20th century, antibiotics have saved many people's lives and completely reversed the passive situation of human helplessness in the face of bacterial diseases.
However, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics has caused the bacteria to quickly adapt to the antibiotic environment and develop resistance.
At the same time, for some serious infections, antibiotic treatment is the only effective treatment.
According to the WHO, the number of deaths caused by bacteria resistant to antibiotics may increase to 10 million a year by 2050, equivalent to one death every three seconds, and equivalent to the number of deaths due to cancer in 2022[1].
Therefore, how to strictly limit the use of antibiotics and delay antibiotic resistance has become an important clinical topic.
Through drug sensitivity detection to select antibiotics that accurately target bacteria and prevent the further development of bacterial resistance have become the key point of China's "precision medical".
1. What is drug sensitivity testing?
Drug sensitivity test is a test to determine the antibacterial or bactericidal ability of drugs in vitro, to use drugs accurately and effectively for treatment.
An antibiotic is said to be "sensitive" to a pathogen that can be suppressed or killed in a very small dose. Otherwise, it is called "insensitive" or "resistant."

2. The importance of drug sensitivity test
For clinical bacterial infections, the abuse of antibiotics will cause serious consequences. For example, if a person is just a common bacterial infection, to make the symptoms disappear quickly he used broad-spectrum antibiotics to make the symptoms disappear quickly. The pathogenic bacteria in the body will be not only killed, but also harm the harmonious coexistence of beneficial bacteria in the body, which may lead to the imbalance of human flora and a variety of harmful bacteria into human body, and even cause more serious consequences:
√ The abuse of many broad-spectrum antibiotics has led to the emergence of many drug-resistant bacteria and even superbugs.
√ Infected people range from young healthy people to elderly people with underlying diseases, as well as people who have been using hormones, immunosuppressants, radiotherapy and chemotherapy for a long time, so clinical symptoms are often atypical.
The emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, especially multi-drug-resistant bacteria, makes clinicians need to choose 1 to 2 antibacterial drugs according to the mechanism of action of antibiotics, and cannot cover common pathogens.
Moreover, different pathogens or different strains of the same pathogen have different sensitivities to the same drug, so the accuracy of drug susceptibility test results is closely related to clinical efficacy.
Therefore, drug sensitivity test has become one of the important means of clinical work.
With the results of drug sensitivity tests as the basis for diagnosis, narrow spectrum antibiotics can be selected as far as possible in clinical work, and the dosage could be controlled just right, which can realize the "precision medicine" and prevent the further spread of bacterial resistance.
3. Microfluidic technology + susceptibility technology
Based on the above factors, the ideal detection technology should have the following characteristics:
√ Fast;
√ Precise;
√ Automation;
√ Phenotypic drug sensitivity can be obtained.
At present, various drug susceptibility detection methods, such as bacterial nanomotor detection technology, flow cytometry technology, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, genome sequencing, single-cell morphological analysis technology, flow cytometry, DNA microarray, multi-chip technology, etc., can only detect drug susceptibility genotypes, but cannot test the drug susceptibility phenotypes. Therefore, it is generally necessary to separate pure colonies for determination, which extends the detection time. This is also the main reason that although many rapid detection technologies of drug resistance genes have been developed, it is difficult to promote clinical application.
Microfluidic technology combines the advantages of "genotype + phenotype" to obtain both molecular detection sensitivity and phenotypic drug sensitivity. The application of biosensors for pathogen detection can detect phenotypic drug sensitivity, and detect the change of bacterial growth status in samples under the action of antibiotics. Electrochemical microfluidics usually target bacterial 16S rRNA to detect changes in current value or fluorescence value and determine the drug-sensitive phenotype (Fig.1)[2].At present, the traditional microbial drug susceptibility detection time is about 48h, while the electrochemical microfluidic system only needs to be monitored after incubation with antibiotics for a short time to directly detect bacterial drug susceptibility in samples, without separating pure colony culture, and can directly apply sample detection to shorten the drug susceptibility detection time to less than 3h. Moreover, the multi-channel chip system can realize multiple detection.
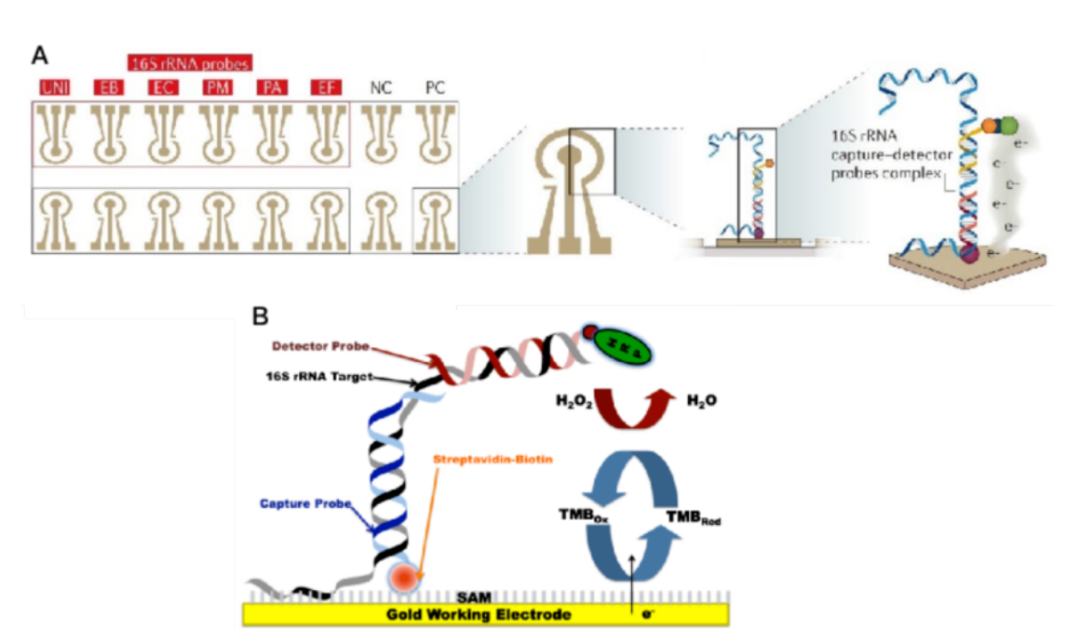
Fig.1 Principle of electrochemical microfluidics technology
Note: Figure A shows the structure of the detection chip. The chip is coated with a variety of bacterial species-specific capture probes, which combine with bacterial 16S rRNA and detection probes to form a specific capture probe-16S RRNA-capture probe complex.
Figure B is the local amplification which shows that the complex structure generates current under the action of the enzyme substrate. Finally, the pathogen type and quantitative judgment can be made by measuring the current signal value.
Quote from CN-HEALTHCARE (https://www.cn-healthcare.com/)
Results shows that microfluidic drug sensitivity technology meets the important factors of rapid, accurate and phenotypic drug sensitivity detection required by clinical practice. While improving the clinical treatment effect, it meets the requirements of China's "precision medical" and has broad development and application prospects in clinical medicine.
[1] Lord Jim O'Neill, UK Treasury Secretary and renowned economist, 《Global Review of Antimicrobial Resistance》, 2016.5.18
[2] Li Xue, 《Application and Problems of Microfluidic Technology in Rapid Pathogen Identification and Drug Susceptibility Detection》,《Clinical Laboratory》, April 2023, "Clinical microbiological Examination"