000
1. Applications of "Gated" Modules
Scenario 1: LiDAR Monitoring of Seawater Pollution
When the laser illuminates seawater, it causes scattered light due to pollution and fluorescence from chlorophyll in plankton, enabling the detection of these objects' distribution. However, reflections from the water surface, air particles, or unknown substances in the ocean create significant background radiation. If monitoring must occur during the day, sunlight is also a background light source. In such scenarios, the "gated" module can be turned on only when the target light signal arrives, significantly reducing the impact of background noise on the detection of target signal.
Scenario 2: Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)
Pulsed laser is used to focus on the surface of the sample to generate plasma, and the composition and concentration information of the measured sample is obtained by analyzing the plasma emission spectrum. However the plasma induced by the laser emits intense bremsstrahlung radiation, which severely disrupts atomic radiation detection. Since the bremsstrahlung radiation duration is short compared to atomic radiation, employing a "gated" module with the appropriate timed opening can eliminate the interference of bremsstrahlung on atomic radiation signal detection.
2. Working Principle of "Gated" Modules
When the photomultiplier tube (PMT) is working normally, the photocathode, multiple dynodes and an anode with sequentially increasing voltages, creating a forward accelerating electric field across each stage. Photoelectrons, under the influence of this field, are multiplied at each dynode before being output as a current at the anode. The switching off principle of gated PMT is to reduce the voltage of a certain stage, reversing the local electric field direction, altering electron trajectories, and preventing their progression to the multiplier system.
3. Introduction to Gated PMT Module Product
Beijing Hamamatsu Photon Techniques Inc. (referred to as Beijing Hamamatsu) produces the CH476 model, a gated photomultiplier tube module. It incorporates a grid structure between the photocathode and dynodes, allowing the module to turn off by lowering the grid voltage, which reverses the field between the grid and photocathode, blocking photoelectron transmission towards the dynodes. Raising the grid voltage restores the forward acceleration field, turning the PMT back on.
Based on the special PMT grid structure and the design of gate circuit, CH476 module realizes the fast gate rise time of 100 ns. Detailed performance parameters are listed in Table 1.①
Note ①:Beijing Hamamatsu offers customization services based on customer requirements.
Table 1 Parameters of Gated PMT Modules
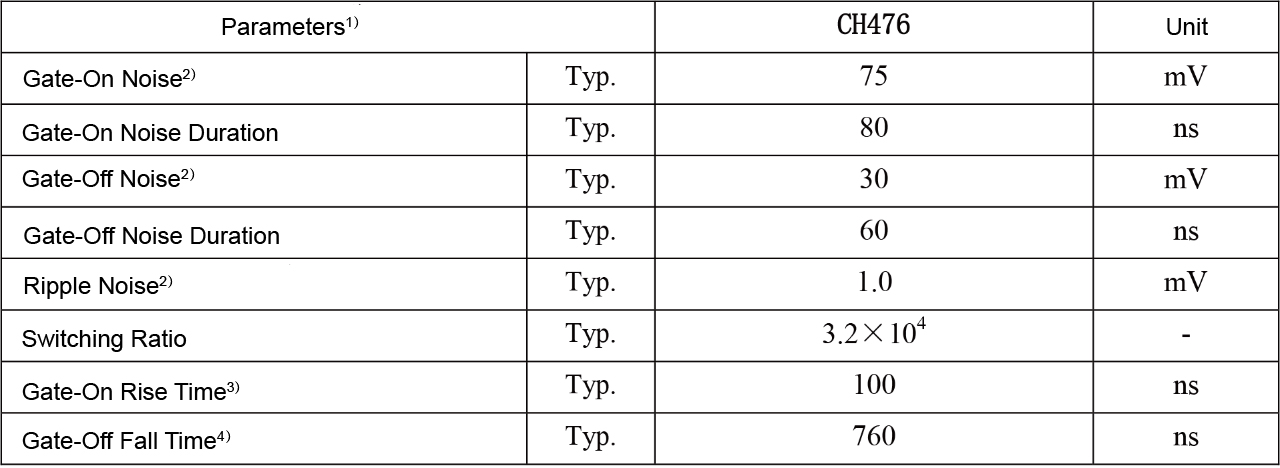
Note:
1)Test Conditions:
a) Gate signal: ±5 V,100 Hz,duty cycle 99.9%, low level on,high level off,that is the gate width is 10 μs.
b) Light source signal: 100 Hz, pulse width 500 ns.
2) Load resistance = 51 Ω(peak to peak).
3) the time from 10% of the falling edge of the gated signal to 90% of the output amplitude of the PMT anode;
4) the time from 10% of the gated signal's rising edge to 10% of the PMT anode's output amplitude.
FIG. 1 Detector Module Products
Beijing Hamamatsu, equipped with interdisciplinary teams in electronics, software, mechanical design, physics, optics, materials, etc., focuses on product quality throughout the R&D and manufacturing process. The company has always been committed to providing customers with the overall solution of light detection and radiation detection,, striving for advanced domestic detector modules and technologies (see FIG. 1). The products have been widely used in medical diagnosis, environmental protection, security check, radiation detection, oil exploration and logging, academic and many other fields.