000
Principle and Composition
When ionizing radiation rays are incident on the scintillator, the scintillator will produce fluorescence with a short decay time, called scintillation light. For example, γ-rays interact with the scintillator to produce three effects: photoelectric effect, Compton effect and electron pair generation effect. The probability of these effects varies depending on the kind of scintillator and the energy of the γ-rays.
In the low energy region of γ-rays, the photoelectric effect dominates, but in the high energy region, the influence of the electron pair generation effect becomes larger. In the photoelectric effect, the amount of fluorescence produced by the photoelectric effect is proportional to the energy of the γ-rays because all the energy of the γ-rays is given to the orbital electron. And the output charge of the PMT is proportional to the received quantity of light, so the output pulse amplitude of the PMT is proportional to the energy of the rays. Correspondingly, a scintillation detector composed of a scintillator and a PMT can know the energy and radiation intensity of the rays by measuring the amplitude and count rate of the output pulse of the PMT.
There are two measurement methods in scintillation counting: One is the energy spectrum analysis method that uses the pulse height analyzer to measure the energy spectrum, the other is the counting method that does not use the pulse height analyzer.
A typical schematic diagram of the scintillation counting method is shown in Fig. 1.
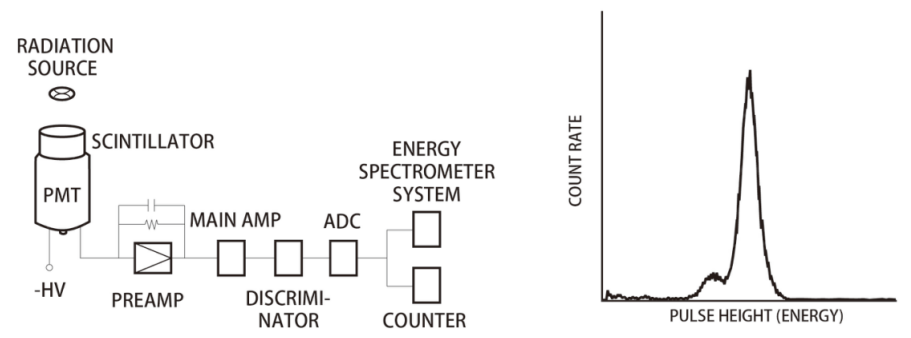
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of scintillation counting method and pulse height distribution
Performance Characteristics
Energy resolution
The ability to discriminate different pulse amplitudes is a very important feature in the energy spectrum analysis. This characteristic is usually evaluated by energy resolution or pulse amplitude resolution.
Energy resolution is defined by the following formula and Fig. 2, generally expressed as a percentage.
R=△P/P
Where R is the energy resolution, P is the photoelectric peak, and △P is the width at half of the height [width at half (H/2) of the peak height (H)].
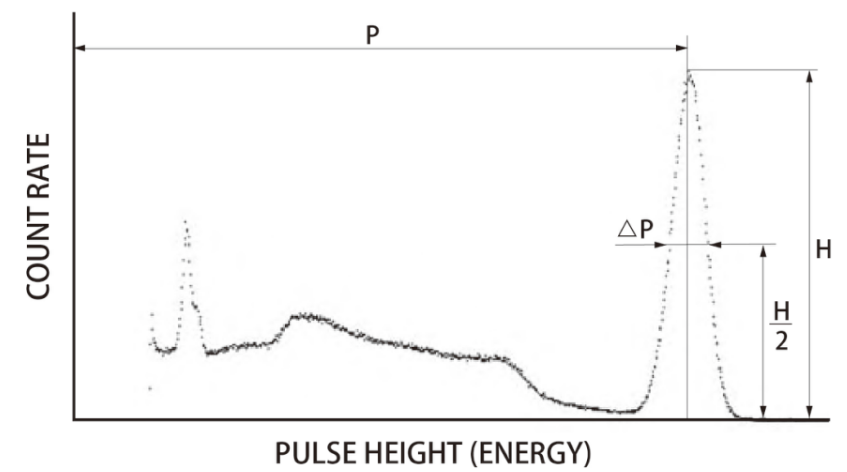
Fig. 2 Definition of energy resolution
Background count
In the scintillation counting, pulse signals are usually generated simultaneously by several photoelectrons. The amplitude of the signal pulse is larger than most of the dark noise pulse amplitudes, so a pulse amplitude discriminator can be used to remove most of the dark noise pulses with small amplitude. It is a main problem that the noise signal with high pulse amplitude is mistaken for pulse signal in the scintillation counting test, so it should be removed by discrimination method.
High pulse amplitude noise is mainly caused by cosmic rays and is a problem at low levels of radioactivity testing. The borosilicate glass used in the PMT contains 40K and the γ-ray energy is 1.46 MeV. There are also radioactive impurities of the U and Th series, which is also the cause of high amplitude impulse noise. The PMTs used in high-energy physics experiments are required to be made of materials with very low radioactive impurities.
In order to shield the influence of cosmic rays, many high-energy physics experiment stations are built in the deep underground that cosmic rays cannot reach. At the same time, the content of radioactive impurities in the PMT is strictly required. This makes it possible to detect subjects with a very low probability of incidence.
Plateau characteristic
The plateau characteristic is an important characteristic in the scintillation counting. The specific meaning is that when the threshold value is fixed, the working voltage of the PMT is increased in a certain area, and the pulse number measured above the threshold value is basically unchanged with the change of applied high voltage, which is usually called plateau. The “plateau” of the scintillation counter is not the characteristic of the PMT, but the characteristic of the scintillation counter under certain conditions. Only when all signal amplitudes output by the PMT is larger than the discrimination threshold but the noise amplitude is less than the discrimination threshold in a certain voltage range, the counting “plateau” is produced. It is obvious that the plateau is related to the nuclear radiation energy, the performance of the scintillator and the PMT, the magnification of the instrument and the threshold of discrimination. Fig. 3 is a plateau characteristic curve using 55Fe and NaI(Tl).
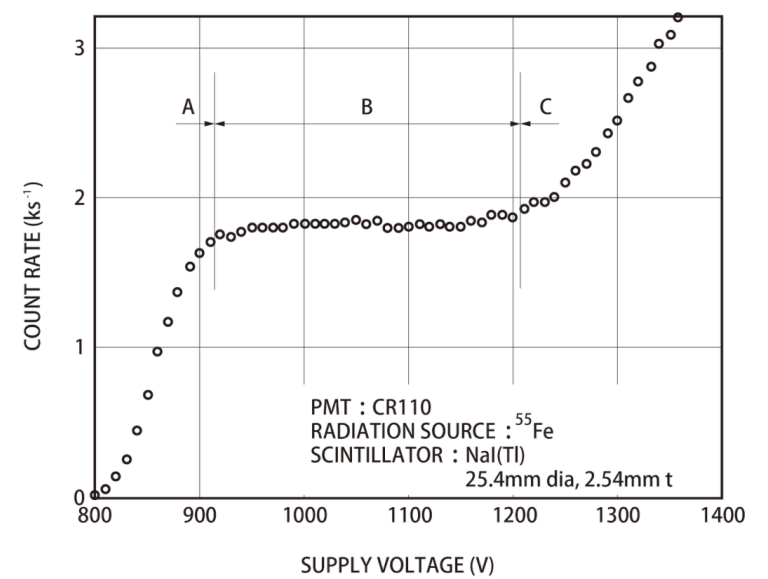
Fig. 3 Plateau characteristic (Combination of 55Fe and NaI(Tl))
When measuring radiation intensity with a scintillation counter, it is important to choose to work on the plateau. Even if the working temperature and performance of the instrument and the PMT are changed to some extent, the instrument can work stably for a long time. In addition, the width of the plateau is not easily affected by changes in output and dark counts.